It is most probable that we to some extent will be eating meat even in the future. Tellus Think Tank meets a passionate pig farmer that runs, what he calls, an eco dynamic breeding – and we investigate some alternative practises to what is labelled organic meat.
Text: Domi Photography: AnnVixen & Nibble Farm
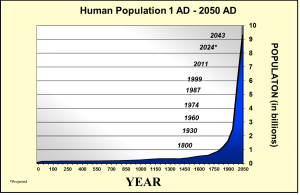
Momentarily we are being hit with the message, from many places and persons in society, that we should completely stop eating meat and become vegetarians. Media reports that livestock is one of the main contributors to greenhouse gas emissions.
We have also learnt that meat is expensive to produce because it requires more land and water than plants do to feed us. The growing population on Earth means that we will need to switch to a plant-based diet and there are no excuses left – all the proteins we need can be found in the more efficient plant kingdom, so why should we torment and eat animals?
Why do humans eat animals?
All people on earth do not eat animals, or at least not meat from certain animals. Hindus avoid eating cow,

Muslims avoid pig, Buddhists avoid any kind of animal, and in many countries people avoid eating dogs and cats.
But why do humans eat animals at all? The historical reason has to do with human survival, of course, as the possibility to feed on animals made it possible to live in places where the plant kingdom, for various reasons has not been sufficient, examples of such sites are numerous:
- Places with geographical limitations such as islands with a growing population have turned instead to the sea and fish.
- Places where the climate does not allowed the plant kingdom to provide food year-round, for example places with long snowy winters or dry periods.
- Places where the kind of vegetation growing, such as grass, can’t feed humans but can feed animals such as cows, pigs, goats and sheep.
There are probably even more reasons to why we eat meat but we can probably agree that animals in many cases have offered mankind an alternative when the plant kingdom has not been sufficient and that from a very early stage of mankind the human diet often has been a mix of plant- and animal based foods.
Animal care is important

It is most likely that the human diet, in part, will continue to be both plant- and animal based. This is why we find it extra important that both agriculture and livestock breeding practises are organic and sustainable and that animals are well taken care of and do not live in misery.
Why is Tellus Think Tank visiting a pig farmer? It is thanks to the flowery descriptions from our local grocery store BEA, at Svedmyra, in Stockholm. The Swedish Christmas tradition includes ham in the oven, instead of a turkey. This Christmas customers could read a large sign above the Christmas ham from Nibble Farm, stating how well the animals were taken care of. On the BEA deli counter Linda, Jenny and Leffe where absolutely enthusiastic about the food from Nibble using phrases such as “tastes better”,
“happy animals” and ” they think differently at Nibble Farm” . This raised our curiosity.
The founder of Nibble Farm
A thin cover of snow lies over the beautiful Swedish Västmanland plains around Nibble Farm the morning I

meet Sven-Erik Johansson. He has over 50 years experience of farming and livestock breeding practises.
A few years ago he passed the responsibility for the farm to the next generation, Magnus and Lena Lindahl. Sven-Erik moved out of the main house of the farm and into a Tiny Home on wheels. He is still working as “Senior Advisor” and daily active in the operational tasks of the farm.
Sven-Erik is 76 years, very sharp and still very engaged and enthusiastic about the development of the farm’s breeding practises. Not only has Sven-Erik built and developed pig-breeding practises on the farm during his career but he also co-founded a hospital practise for spinal recovery – to give you a picture of his capacity. During our conversation, he talked about respecting animals and exploring new and better ways to develop breeding practises.
Sven-Erik’s upbringing, background and life reminds me of Ingvar Kamprad, founder of IKEA, who started off by selling matches to his neighbours. In Sven-Erik’s case, he took over four chickens when he was eight and started selling eggs to teachers and classmates. The proceeds where used to expand both the poultry practise and later to pay for his higher studies. When in his 20’ies he switched to pig farming.
Eco-dynamic Nibble

Nibble Farm breeds 5,000 pigs a year and Sven-Erik describes the development of the eco-dynamic pig practises. One of the farm’s research partners has been the SVA, Swedish National Veterinarian Medical Institution. The research has included filming of pigs to increase the understanding of their needs so that farms can develop operations to fit the pig better. The aim of research has often been to develop practises so that breeding pigs can thrive. It was discovered when filming the pigs that fixed feeding times stressed them immensely. Therefore the farm introduced feeding machines where the pigs could eat whenever they wanted.
Inspiration to develop the practises of the farm has also been sought abroad, much has been learnt from Danish farmers. Legislation in Sweden, however, has been better with an early ban on disease preventing antibiotics, says Sven-Erik.
The Netherlands is also a forerunner in livestock development and Sven-Erik was very impressed by the Dutch company Nedap, with 90 people in their research department working on technology for better animal conditions!
According to Sven-Erik, Nibble Farm runs a mix of breeding practises, positioning their farm between what is

considered pure organic and old fashioned “regular” pig breeding. Nibble calls their practice eco-dynamic and they aim to breed happy pigs that give the meat a great taste. It is equally important that the meat is affordable to everyone. In order to breed happy pigs one important factor is not to rush or stress the animals.
Instead of being visitors Nibble Farm is currently often visited by delegations from around the world– last week they received a delegation from Australia. They are happy to share their ideas on eco-dynamic farming and how the natural cycle of nature is mixed with the farming practises.
Nibble Farm and the natural cycle of nature

Nibble Farm is almost self-sufficient and grows about 90 % of the food needed by their pigs. They aim to run a practise with as little environmental impact as possible in both livestock breeding and agricultural practises and engage in crop rotation to avoid soil depletion, which also reduces the need to add nutrients. The farm also minimizes the use of pesticides, fertilise the soil with natural resources from the pig practise.
They run livestock breeding and agriculture practises in balance with the natural cycle of nature and try to minimize the harmful effects of the farm by, for instance, upgrading the agricultural machinery, such as tractors, to lighter versions to avoid compressing the soil too much.
The tour begins of Nibble Farm begins with the sows and their piglets
I admit to being a true city slicker and that this is the first time I have ever set foot in a real farm. From films

on YouTube I have understood that pig breeding practises are often murky with pigs trapped in dark and confined spaces and running and screaming in fear. Although Sven-Erik has told me that Nibble Farm’s practice differs I still enter expecting the worst.
The newly borns
We visit the sows and their piglets. The contrast between the biting wind outside and the pleasant warmth of this building is palpable. I learn that cold can stress both piglets and sows and that the heat in the building, therefore, is important.

In this large farm room there are about 20 boxes filled with mother-child pig families. Each box is 7 square metres and houses a sow with 12-14 piglets. In addition to the heated building, each box includes a cubbyhole with red heating lamps for the piglets to cuddle under. The sows have special heating tubes to warm them when feeding the piglets. Each box has a pipe throughout it to minimize the risk for the piglets to being squeezed under the sow as she lies down.
We visit one of the boxes and find the piglets to be lively engaged in play with each other. The mother-sow looks tired and a bit discouraged – it must be quite a job to feed 14 piglets. Sven-Erik says that the sow and piglets remain in the box for 31 days after farrowing, i.e. the actual birth. The sow can eat whenever she wants and doesn’t need to wait for fixed meal times, which reduces the stress that the pigs would otherwise experience. Sven-Erik says that this is why we do not hear any screams, the pigs are not stressed, eat when they want and are warm and comfortable. Undeniably, even though the sows are understandably tired, the piglets seem to thrive.
31 days old – time to leave home
Next stop we make is with piglets between 31 and 70 days old. They live together in a different building and are

kept indoors to keep their warmth. It turns out to be a fun visit on our tour of the farm as we visit 50 piglets in a 100 square meter box. They can eat when they want and also have a heating lamp to warm them. However, they seem not at all interested in the lamps as they playfully run around in groups in a style that resembles a tiny soccer team. I’m no pig expert but when I see these pigs, I perceive them to be happy!
Between the ages of two and six months the pigs move into the farm’s most recently built stables where they share a box with about 20 other pigs. This is the last station for them on the farm. The boxes do not look very inspiring but the pigs can eat when they want and if they want to go outdoors they have their own balcony. In the summer the balcony even holds a shower so they can cool down!

Again, I see pigs looking curious and happy. Sven-Erik tells me a few surprising things about the pig. One is that they do not like to stand in hot sun because of their weak pigmentation and lack of protective hair. The pig is one of the cleanliest animals. After researching the area, Nibble Farm now know that pigs prefer the shade and a cool water shower before taking a role in the mud and have designed the farm accordingly.
Not even one bad day
At six months of age, it is time for the pigs’ journey to the slaughterhouse in Skövde.
-So, Pigs only have one bad day? I ask.
-No, they do not even have one bad day! Sven-Erik responds.
He explains that the pigs move in a very easy and stress-less way into the transportation truck and that they quickly fall asleep during the journey as they feel safe and are still together with their siblings. Once at the slaughterhouse, they are calmly moved into a one-pig-at-a-time elevator and sedated prior to the actual slaughter.
During their lifetime they are never separated from their siblings.
The sows in waiting
The last building we visit on our tour is a classic Swedish Falu-red barn. It is one of the most beautiful places

I’ve visited and the air inside is fresh and cool, the birds are chirping in the rafters, and the airy walls let in a beautiful pattern of glorious daylight. The sows live here during their three months pregnancy and it looks very harmonious.
The sows can choose if they want to be in their outdoor courtyard or stay in the straw filled barn. The sow quarters have been designed so they can move around freely and exercise during their pregnancy. During my visit the weather is dull and most decide to stay indoors snuggle down in thick layers of straw. Some are curious and greet us upon arrival and when we go to look at their concrete yard some of them follow us out!
The Nibble pig feed
Nibble Farm grows 90 % of their pigs food. The food consists of roughage (hay), herbs such as camomile, bird’s-foot-trefoil and catsfoot but also peas, broad beans , linseed cake, rape seed and cereals. The last ten per cent of the diet consists of various nutritional supplements.
Nibble eco-dynamic farming compared to organically labelled breeding
 Swedes consumers find several different kinds of sustainable labelled food and the one that is the most difficult to produce is KRAV. Another widely used organic label is the EU organic logo, which is usually somewhat easier to produce.
Swedes consumers find several different kinds of sustainable labelled food and the one that is the most difficult to produce is KRAV. Another widely used organic label is the EU organic logo, which is usually somewhat easier to produce.
Here are some examples of organic requirements that Nibble Farm follows:

The pig should be able to go outdoors at any time of the year. The pig should always have the possibility to root. During hot weather the pig should be able to cool off. The farm should be self-sufficient up to 50% of their pigs’ food (Nibble produces 90%). The pig should have free access to a bed of hay. Pigs should not routinely be given preventive treatment with antibiotics. During castration male pigs have to be provided with anaesthesia and analgesics.
Nibble Farm has chosen to deviate from some organic label requirement and Sven-Erik explains why:
- According to some organic requirements pigs must obtain field grazing in the summer and have large areas to move around. Nibble Farm doesn’t provided this and Sven-Erik explains that for centuries pigs have become accustomed to a life indoors, that their pigment can’t handle strong sun and they don’t like to protect themselves from the sun by rolling in mud. Therefore, the animals have the ability to go out but they always have the opportunity to go back indoors and during summer they can take a cooling shower whenever they want.
- According to the current organic requirements sows should be allowed to build nests. Nibble considered that pigs’ nests require so much straw that many piglets are “lost” in it and more easily squeezed to death. The sows are instead presented with enough straw to be able to make a nice bed and a heat lamp as a replacement to a full nest.
- Additional organic requirements state the pig should only eat organically grown food, not treated with any chemical pesticides. Nibble Farm want both plants and animals to be healthy and therefore use pesticides when needed but not routinely. Pigs are also vaccinated to prevent disease but are not given

The tasty and happy pig is one of the aims of the eco-dynamic farm. Photo: AnnVixen antibiotics regularly.
I understand that there are discussion about which approach should be accepted in the livestock industry,
ranging from “ordinary” to strictly organic according to official guidelines.
Nibble Farm has chosen its own path and conducted research in areas that have not seemed apparent to others, respecting the cycle of nature in balance with the urge to produce good meat affordable to the many.
My day at Nibble Farm is coming to an end and we pass the silo, the storage of the self-grown animal food, and the farmhouse where the air-dried hams and salami hang. During summertime Nibble Farm opens for visitors – I would recommend anyone that wishes to learn more to drop by!
To summarize my day at Nibble Farm it has been informative and full of happy and curious pigs!
If we are to continue eating meat in the future I believe every farm should be breeding happy animals.
Do you want to read more about the future of food, check out the skyscrapers that will feed city dwellers with vegetables!
Let Tellus Think Tank notify you when our next article is available…